Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
A brief overview
Introduction
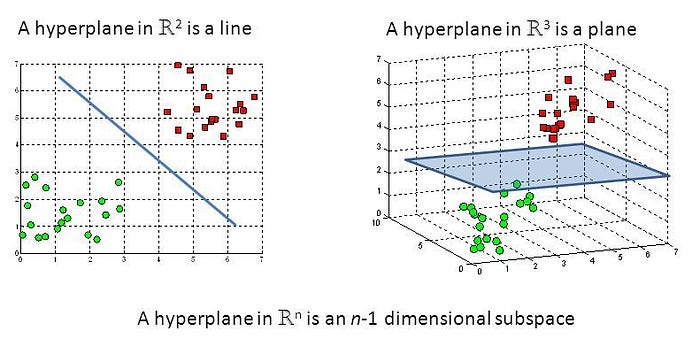
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are a set of supervised learning methods which learn from the dataset and can be used for both regression and classification. An SVM is a kind of large-margin classifier: it is a vector space based machine learning method where the goal is to find a decision boundary between two classes that is maximally far from any point in the training data.
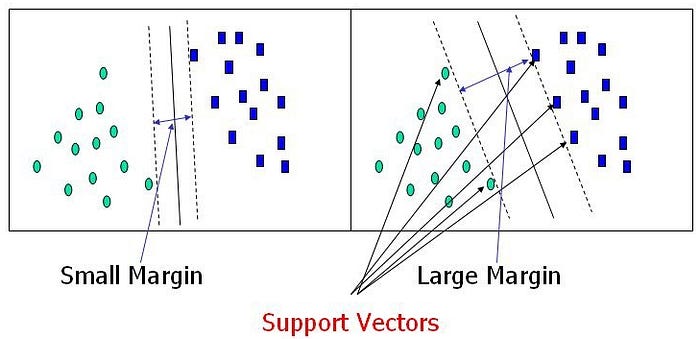
Support Vectors :
The term Support Vectors refers to the co-ordinates of individual observation. Support Vector Machine is a frontier which best segregates the two classes using a hyperplane/ line.
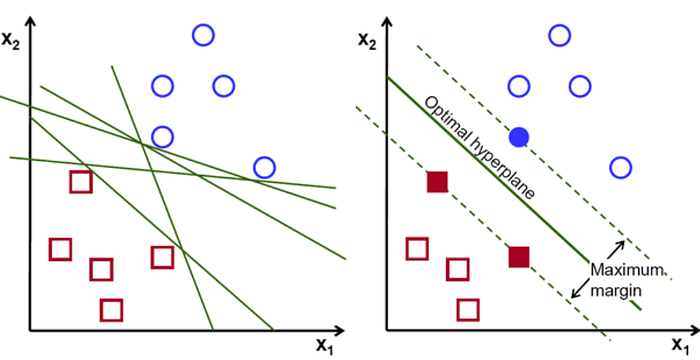
Working of SVM :
An SVM model is a representation of the examples as points in space, mapped so that the examples of the separate categories are divided by a clear gap that is as wide as possible. New examples are then mapped into that same space and predicted to belong to a category based on which side of the gap they fall.
In addition to performing linear classification, SVMs can efficiently perform a non-linear classification using what is called the kernel trick, implicitly mapping their inputs into high-dimensional feature spaces.
Kernel Method :
Kernel method is used by SVM to perform a non-linear classification. They take low dimensional input space and convert them into high dimensional input space. It converts non-separable classes into the separable one, it finds out a way to separate the data on the basis of the data labels defined by us.
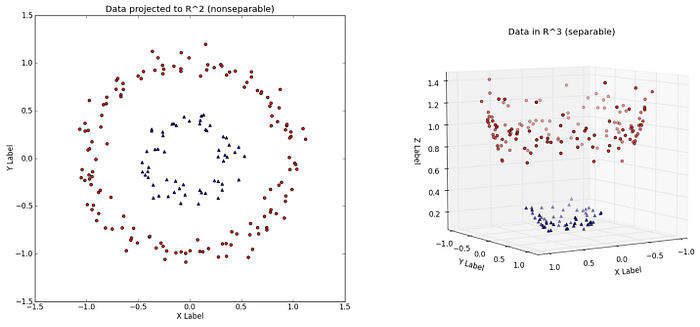
Features and Advantages of SVMs :
- They maximize the margin of the decision boundary using quadratic optimization techniques which find the optimal hyperplane.
- It has the ability to handle large feature spaces.
- SVM’s are very good when we have no idea about our data.
- Works well with even unstructured and semi-structured data like text, Images and trees.
- The kernel trick is real strength of SVM. With an appropriate kernel function, we can solve any complex problem.
- It scales relatively well to high dimensional data.
- SVM models have generalization in practice, the risk of over-fitting is less in SVM.
Limitations of SVM :
- It is sensitive to noise.
- The extension of classification to more than two classes is problematic.
- Choosing a “good” kernel function is not easy.
- Long training time for large datasets.
- Difficult to understand and interpret the final model, variable weights and individual impact.
- Since the final model is not so easy to see, we can not do small calibrations to the model hence its tough to incorporate our business logic.
- The SVM hyper parameters are Cost -C and gamma. It is not that easy to fine-tune these hyper-parameters. It is hard to visualize their impact
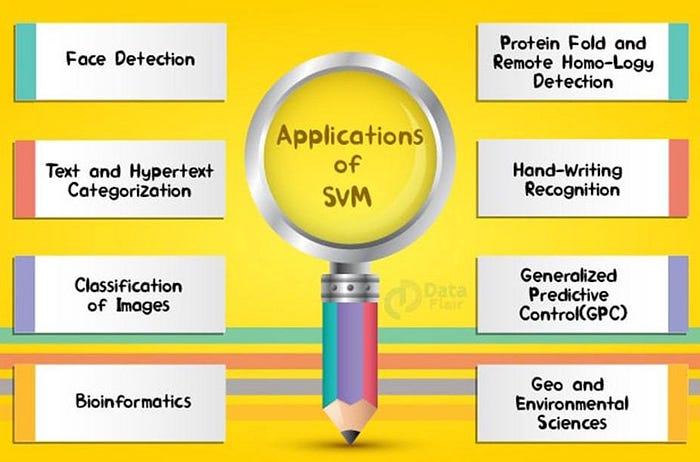
Some applications of SVM :
- Text (and hypertext) categorization.
- Image Classification.
- Bioinformatics (Protein classification, Cancer classification).
- Hand-written character recognition.
- Determination of SPAM email.
- Time Series Analysis.
- Anomaly Detection.