Random Forest Classification
Along with its implementation in Python
In this blog we’ll try to dig deeper into Random Forest Classification. Here we will learn about ensemble learning and will try to implement it using Python.
You can find the code over here.
Random Forest Classifier :
It is an ensemble tree-based learning algorithm. The Random Forest Classifier is a set of decision trees from randomly selected subset of training set. It aggregates the votes from different decision trees to decide the final class of the test object.
Ensemble Algorithm :
Ensemble algorithms are those which combines more than one algorithms of same or different kind for classifying objects. For example, running prediction over Naive Bayes, SVM and Decision Tree and then taking vote for final consideration of class for test object.
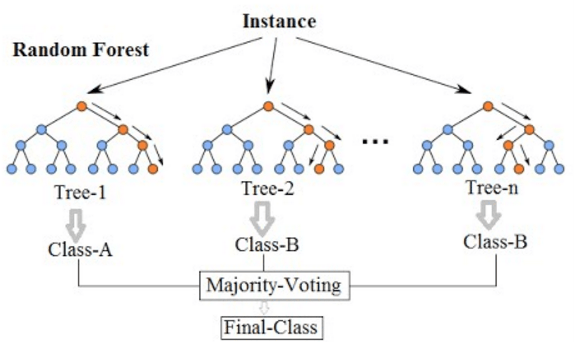
Types of Random Forest models:
- Random Forest Prediction for a classification problem: f(x) = majority vote of all predicted classes over B trees
- Random Forest Prediction for a regression problem: f(x) = sum of all sub-tree predictions divided over B trees
An Example of Random Forest Classification :
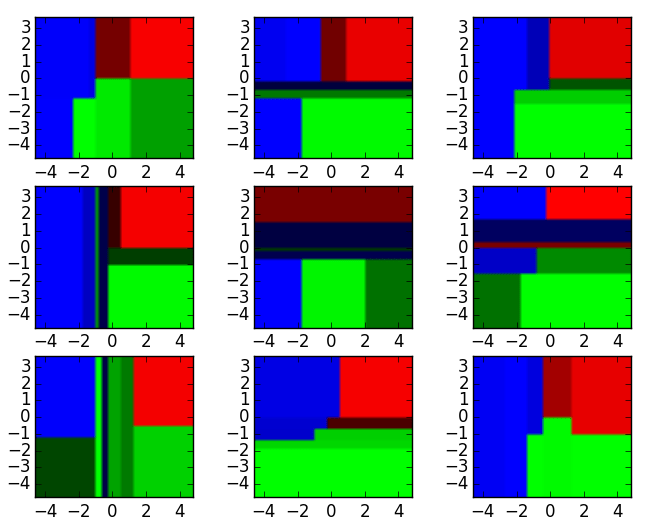
Nine Different Decision Tree Classifiers
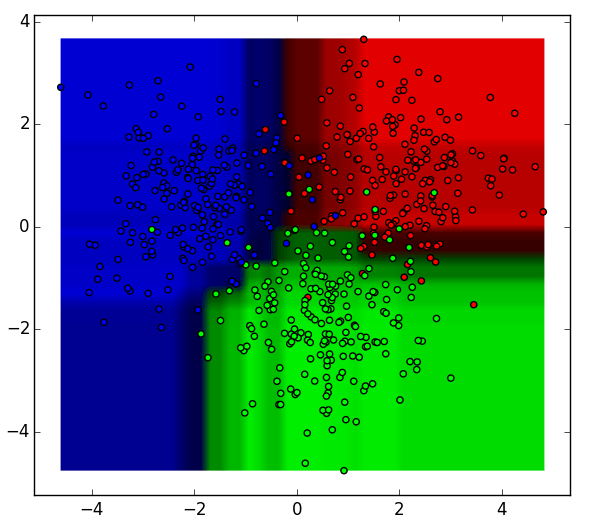
The 9 decision tree classifiers shown above can be aggregated into a random forest ensemble which combines their input (on the right). The horizontal and vertical axes of the above decision tree outputs can be thought of as features x1 and x2. At certain values of each feature, the decision tree outputs a classification of “blue”, “green”, “red”, etc.
These above results are aggregated, through model votes or averaging, into a single ensemble model that ends up outperforming any individual decision tree’s output.
Features and Advantages of Random Forest :
- It is one of the most accurate learning algorithms available. For many data sets, it produces a highly accurate classifier.
- It runs efficiently on large databases.
- It can handle thousands of input variables without variable deletion.
- It gives estimates of what variables that are important in the classification.
- It generates an internal unbiased estimate of the generalization error as the forest building progresses.
- It has an effective method for estimating missing data and maintains accuracy when a large proportion of the data are missing.
Disadvantages of Random Forest :
- Random forests have been observed to overfit for some datasets with noisy classification/regression tasks.
- For data including categorical variables with different number of levels, random forests are biased in favor of those attributes with more levels. Therefore, the variable importance scores from random forest are not reliable for this type of data.
Implementation of Random Forest Classification on real life dataset:
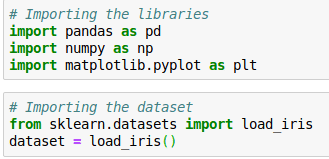
1. Importing Python Libraries and Loading our Dataset into a Data Frame
2. Splitting our dataset into training set and test set
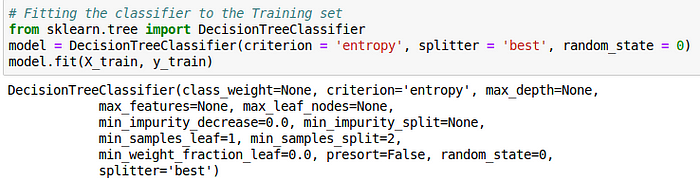
3. Creating a Random Forest Classification model and fitting it to the training data

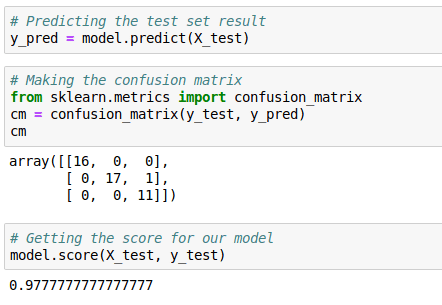
4. Predicting the test set results and making the Confusion matrix
Conclusion :
In this blog we have learned about the Random forest classifier and its implementation. We looked at the ensembled learning algorithm in action and tried to understand what makes Random Forest different from other machine learning algorithms.
